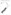Boulderfields of acidic rocks (non-volcanic)
In this section
-
Inland & alpine
- Basic cliffs, scarps and tors
- Boulderfields of acidic rocks (non-volcanic)
- Boulderfields of calcareous rocks
- Braided riverbeds
- Calcareous cliffs, scarps and tors
- Calcareous screes
- Cliffs, scarps and tors of acidic rocks
- Cliffs, scarps and tors of quartzose rocks
- Cloud forests
- Frost hollows
- Granitic gravel fields
- Granitic sand plains
- Inland outwash gravels
- Inland saline (salt pans)
- Inland sand dunes
- Limestone erosion pavements
- Moraines
- Old tephra (>500 years) plains (= frost flats)
- Recent lava flows
- Sandstone erosion pavements
- Screes of acidic rocks
- Strongly leached terraces and plains
- Ultrabasic boulderfields
- Ultrabasic cliffs, scarps and tors
- Ultrabasic hills
- Ultrabasic screes
- Volcanic boulderfields
- Volcanic debris flows or lahars
- Volcanic dunes
- Young tephra plains and hillslopes

Granite boulderfield, Lookout Range, NW Nelson (Susan Wiser)
Boulderfields are a collection of very large fragments of fallen detritus that have accumulated at the foot of a slope. Areas can appear similar to moraine (material deposited by glaciers). Granite and greywacke are the most common parent rocks. For many years, lichens and mosses may be the only colonists, particularly in alpine areas. Over time, boulderfields may be invaded from the margins by rhizomatous plants such as ferns and lianes. Older boulder fields at lower elevations may support woody species (e.g. snow totara) and communities (e.g. grey scrub and associated small trees), and provide fire breaks that allow remnants of vegetation to persist in otherwise disturbed landscapes. Pockets of fines can provide shaded, mesic habitats that allow herbaceous plants to persist.
Synonyms
Boulderfields of silicic rocks
Notable flora and fauna
Threatened and rare plants include nationally critical Myosotis albosericea, nationally endangered Veronica cupressoides, the declining coral broom (Carmichaelia crassicaulis subsp. crassicaulis), North Westland snow tussock (Chionochloa juncea), Olearia lineata and Coprosma intertexta.
Threat status
Not threatened (Holdaway et al. 2012)
Threats
Browsing animals (goats, deer, tahr, chamois, hares and, possums) are likely to be present at some sites.
Where do they occur?
On most granitic and greywacke mountain ranges in the South Island.
Further reading
Wardle P 1991. Vegetation of New Zealand. Cambridge University Press. Pp 194.
Wardle P 2001. Distribution of native forest in the upper Clutha district, Otago, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Botany 39: 435-446.